Building blocks of HTML
An HTML document consist of its basic building blocks which are:
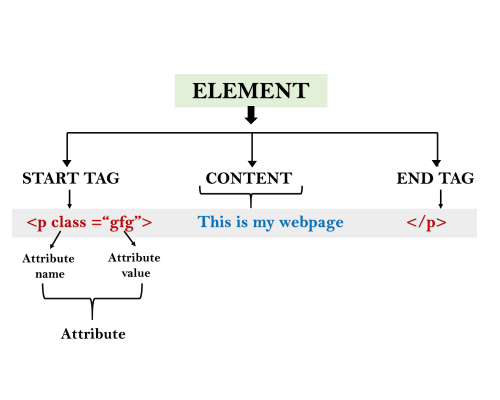
- Tags: An HTML tag surrounds the content and apply meaning to it. It is written between < and > brackets.
- Attribute: An attribute in HTML provides extra information about the element, and it is applied within the start tag. An HTML attribute contains two fields: name & value.
Syntax
- Elements: An HTML element is an individual component of an HTML file. In an HTML file, everything written within tags are termed as HTML elements.
Example:
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>The basic building blocks of HTML</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <h2>The building blocks</h2>
- <p>This is a paragraph tag</p>
- <p style="color: red">The style is attribute of paragraph tag</p>
- <span>The element contains tag, attribute and content</span>
- </body>
- </html>
Output:
The building blocks
This is a paragraph tag
The style is attribute of paragraph tag
The element contains tag, attribute and contentHTML tags are like keywords which defines that how web browser will format and display the content. With the help of tags, a web browser can distinguish between an HTML content and a simple content. HTML tags contain three main parts: opening tag, content and closing tag. But some HTML tags are unclosed tags.
When a web browser reads an HTML document, browser reads it from top to bottom and left to right. HTML tags are used to create HTML documents and render their properties. Each HTML tags have different properties.
An HTML file must have some essential tags so that web browser can differentiate between a simple text and HTML text. You can use as many tags you want as per your code requirement.
- All HTML tags must enclosed within < > these brackets.
- Every tag in HTML perform different tasks.
- If you have used an open tag <tag>, then you must use a close tag </tag> (except some tags)
Syntax
<tag> content </tag>
HTML Tag Examples
Note: HTML Tags are always written in lowercase letters. The basic HTML tags are given below:
<p> Paragraph Tag </p>
<h2> Heading Tag </h2>
<b> Bold Tag </b>
<i> Italic Tag </i>
<u> Underline Tag</u>
Unclosed HTML Tags
Some HTML tags are not closed, for example br and hr.
<br> Tag: br stands for break line, it breaks the line of the code.
<hr> Tag: hr stands for Horizontal Rule. This tag is used to put a line across the webpage.
HTML Meta Tags
DOCTYPE, title, link, meta and style
HTML Text Tags
<p>, <h1>, <h2>, <h3>, <h4>, <h5>, <h6>, <strong>, <em>, <abbr>, <acronym>, <address>, <bdo>, <blockquote>, <cite>, <q>, <code>, <ins>, <del>, <dfn>, <kbd>, <pre>, <samp>, <var> and <br>
HTML Link Tags
<a> and <base>
HTML Image and Object Tags
<img>, <area>, <map>, <param> and <object>
HTML List Tags
<ul>, <ol>, <li>, <dl>, <dt> and <dd>
HTML Table Tags
table, tr, td, th, tbody, thead, tfoot, col, colgroup and caption
HTML Form Tags
form, input, textarea, select, option, optgroup, button, label, fieldset and legend
HTML Scripting Tags
script and noscript
Note: We will see examples using these tags in later charters.
HTML Tags List
Following is the complete list of HTML tags with the description which are arranged alphabetically.
Note: Here  represents newly added Elements in HTML5.
represents newly added Elements in HTML5.
HTML Tags by Alphabets
| Tag name | Description |
|---|---|
| <!-- --> | This tag is used to apply comment in an HTML document. |
| <!DOCTYPE> | This tag is used to specify the version of HTML |
| A | |
| <a> | It is termed as anchor tag and it creates a hyperlink or link. |
| <abbr> | It defines an abbreviation for a phrase or longer word. |
| <acronym> | It defines acronym for a word. (Not supported in HTML5) |
| <address> | It defines the author's contact information of the HTML article |
| <applet> | It defines an embedded Java applet. (Not supported in HTML5) |
| <area> | It defines the area of an image map. |
<article> | It defines the self-contained content. |
<aside> | It defines content aside from main content. Mainly represented as sidebar. |
<audio> | It is used to embed sound content in HTML document. |
| B | |
| <b> | It is used to make a text bold. |
| <base> | This tag defines the base URL for all relative URL within the document. |
| <basefont> | This tag is used to set default font, size and color for all elements of document. (Not supported in HTML5) |
<bdi> | This tag is used to provide isolation for that part of text which may be formatted in different directions from its surrounding text. |
| <bdo> | It is used to override the current text direction. |
| <big> | This tag is used to make font size one level larger than its surrounding content. (Not supported in HTML5) |
| <blockquote> | It is used to define a content which is taken from another source. |
| <body> | It is used to define the body section of an HTML document. |
| <br> | It is used to apply single line break. |
| <button> | It is used to represent a clickable button |
| C | |
<canvas> | It is used to provide a graphics space within a web document. |
| <caption> | It is used to define a caption for a table. |
| <center> | It is used to align the content in center. (Not supported in HTML5) |
| <cite> | It is used to define the title of the work, book, website, etc. |
| <code> | It is used to display a part of programming code in an HTML document. |
| <col> | It defines a column within a table which represent common properties of columns and used with the <colgroup> element. |
| <colgroup> | It is used to define group of columns in a table. |
| D | |
<data> | It is used to link the content with the machine-readable translation. |
<datalist> | It is used to provide a predefined list for input option. |
| <dd> | It is used to provide definition/description of a term in description list. |
| <del> | It defines a text which has been deleted from the document. |
<details> | It defines additional details which user can either view or hide. |
| <dfn> | It is used to indicate a term which is defined within a sentence/phrase. |
<dialog> | It defines a dialog box or other interactive components. |
| <dir> | It is used as container for directory list of files. (Not supported in HTML5) |
| <div> | It defines a division or section within HTML document. |
| <dl> | It is sued to define a description list. |
| <dt> | It is used to define a term in description list. |
| E | |
| <em> | It is used to emphasis the content applied within this element. |
<embed> | It is used as embedded container for external file/application/media, etc. |
| F | |
| <fieldset> | It is used to group related elements/labels within a web form. |
<figcaption> | It is used to add a caption or explanation for the <figure> element. |
<figure> | It is used to define the self-contained content, and s mostly refer as single unit. |
| <font> | It defines the font, size, color, and face for the content. (Not supported in HTML5) |
<footer> | It defines the footer section of a webpage. |
| <form> | It is used to define an HTML form. |
| <frame> | It defines a particular area of webpage which can contain another HTML file. (Not supported in HTML5) |
| <frameset> | It defines group of Frames. (Not supported in HTML5) |
| H | |
| <h1> to <h6> | It defines headings for an HTML document from level 1 to level 6. |
| <head> | It defines the head section of an HTML document. |
<header> | It defines the header of a section or webpage. |
| <hr> | It is used to apply thematic break between paragraph-level elements. |
| <html> | It represents root of an HTML document. |
| I | |
| <i> | It is used to represent a text in some different voice. |
| <iframe> | It defines an inline frame which can embed other content. |
| <img> | It is used to insert an image within an HTML document. |
| <input> | It defines an input field within an HTML form. |
| <ins> | It represent text that has been inserted within an HTML document. |
| <isindex> | It is used to display search string for current document. (Not supported in HTML5) |
| K | |
| <kbd> | It is used to define keyboard input. |
| L | |
| <label> | It defines a text label for the input field of form. |
| <legend> | It defines a caption for content of <fieldset> |
| <li> | It is used to represent items in list. |
| <link> | It represents a relationship between current document and an external resource. |
| M | |
<main> | It represents the main content of an HTML document. |
| <map> | It defines an image map with active areas. |
<mark> | It represents a highlighted text. |
| <marquee> | It is used to insert the scrolling text or an image either horizontally or vertically. (Not supported in HTML5) |
| <menu> | It is used for creating a menu list of commands. |
| <meta> | It defines metadata of an HTML document. |
<meter> | It defines scalar measurement with known range or fractional value. |
| N | |
<nav> | It represents section of page to represent navigation links. |
| <noframes> | It provides alternate content to represent in browser which does not support the <frame> elements. (Not supported in HTML5) |
| <noscript> | It provides an alternative content if a script type is not supported in browser. |
| O | |
| <object> | It is used to embed an object in HTML file. |
| <ol> | It defines an ordered list of items. |
| <optgroup> | It is used to group the options of a drop-down list. |
| <option> | It is used to define options or items in a drop-down list. |
<output> | It is used as container element which can show result of a calculation. |
| P | |
| <p> | It represents a paragraph in an HTML document. |
| <param> | It defines parameter for an <object> element |
<picture> | It defines more than one source element and one image element. |
| <pre> | It defines preformatted text in an HTML document. |
<progress> | It defines the progress of a task within HTML document. |
| Q | |
| <q> | It defines short inline quotation. |
| R | |
<rp> | It defines an alternative content if browser does not supports ruby annotations. |
| <rt> | It defines explanations and pronunciations in ruby annotations. |
| <ruby> | It is used to represent ruby annotations. |
| S | |
| <s> | It render text which is no longer correct or relevant. |
| <samp> | It is used to represent sample output of a computer program. |
| <script> | It is used to declare the JavaScript within HTML document. |
<section> | It defines a generic section for a document. |
| <select> | It represents a control which provides a menu of options. |
| <small> | It is used to make text font one size smaller than document?s base font size. |
<source>> | It defines multiple media recourses for different media element such as <picture>, <video>, and <audio> element. |
| <span> | It is used for styling and grouping inline. |
| <strike> | It is used to render strike through the text. (Not supported in HTML5) |
| <strong> | It is used to define important text. |
| <style> | It is used to contain style information for an HTML document. |
| <sub> | It defines a text which displays as a subscript text. |
<summary> | It defines summary which can be used with <details> tag. |
| <sup> | It defines a text which represent as superscript text. |
| <svg> | It is used as container of SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics). |
| T | |
| <table> | It is used to present data in tabular form or to create a table within HTML document. |
| <tbody> | It represents the body content of an HTML table and used along with <thead> and <tfoot>. |
| <td> | It is used to define cells of an HTML table which contains table data |
| <template> | It is used to contain the client side content which will not display at time of page load and may render later using JavaScript. |
| <textarea> | It is used to define multiple line input, such as comment, feedback, and review, etc. |
| <tfoot> | It defines the footer content of an HTML table. |
| <th> | It defines the head cell of an HTML table. |
| <thead> | It defines the header of an HTML table. It is used along with <tbody> and <tfoot> tags. |
<time> | It is used to define data/time within an HTML document. |
| <title> | It defines the title or name of an HTML document. |
| <tr> | It defines the row cells in an HTML table |
| <track> | It is used to define text tracks for <audio> and <video> elements. |
| <tt> | It is used to define teletype text. (Not supported in HTML5) |
| U | |
| <u> | It is used to render enclosed text with an underline. |
| <ul> | It defines unordered list of items. |
| V | |
| <var> | It defines variable name used in mathematical or programming context. |
<video> | It is used to embed a video content with an HTML document |
| W | |
<wbr> | It defines a position within text where break line is possible. |
HTML Attribute
- HTML attributes are special words which provide additional information about the elements or attributes are the modifier of the HTML element.
- Each element or tag can have attributes, which defines the behaviour of that element.
- Attributes should always be applied with start tag.
- The Attribute should always be applied with its name and value pair.
- The Attributes name and values are case sensitive, and it is recommended by W3C that it should be written in Lowercase only.
- You can add multiple attributes in one HTML element, but need to give space between two attributes.
Syntax
Example
Output:
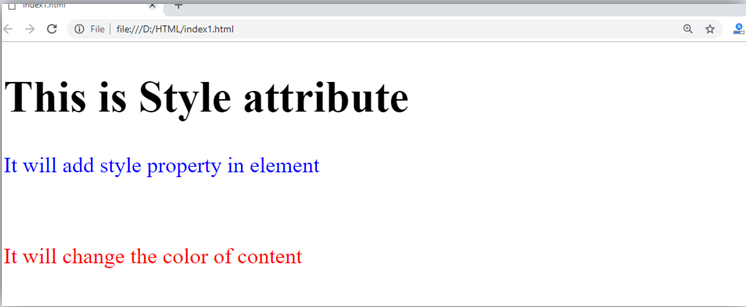
Explanation of above example:
In the above statement, we have used paragraph tags in which we have applied style attribute. This attribute is used for applying CSS property on any HTML element. It provides height to paragraph element of 50px and turns it colour to blue.
In the above statement we have again used style attribute in paragraph tag, which turns its colour red.
Note: There are some commonly used attributes are given below, and the complete list and explanation of all attributes are given in HTML attributes List.
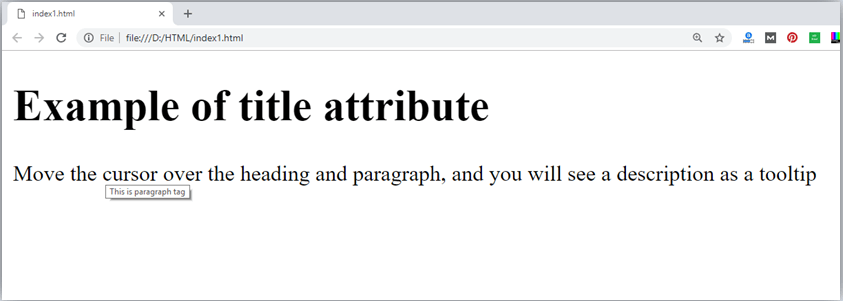
The title attribute in HTML
Description: The title attribute is used as text tooltip in most of the browsers. It display its text when user move the cursor over a link or any text. You can use it with any text or link to show the description about that link or text. In our example, we are taking this with paragraph tag and heading tag.
Example
With <h1> tag:
With <p> tag:
Code:
Output:
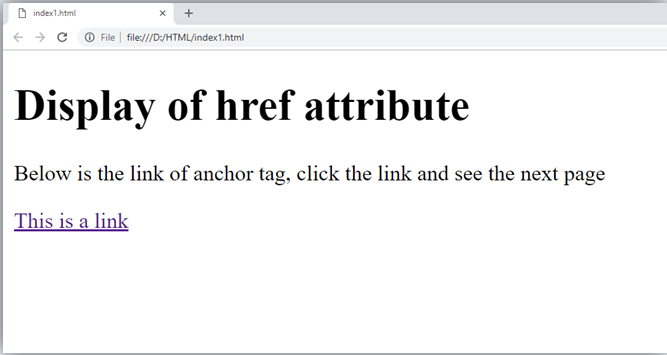
The href attribute in HTML
Description: The href attribute is the main attribute of <a> anchor tag. This attribute gives the link address which is specified in that link. The href attribute provides the hyperlink, and if it is blank, then it will remain in same page.
Example
With link address:
Without link address:
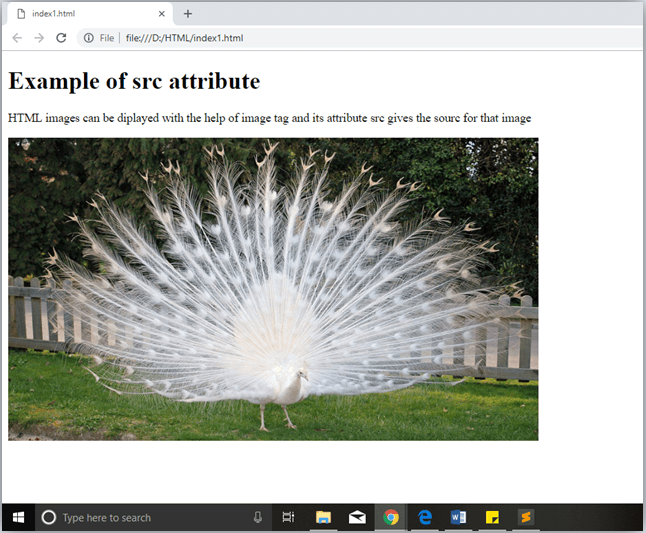
The src Attribute
The src attribute is one of the important and required attribute of <img> element. It is source for the image which is required to display on browser. This attribute can contain image in same directory or another directory. The image name or source should be correct else browser will not display the image.
Example
Note: The above example also have height and width attribute, which define the height and width of image on web page.
Output:
Quotes: single quotes or double quotes?
In this chapter you have seen that, we have used attribute with double quotes, but some people might use single quotes in HTML. So use of single quotes with HTML attribute, is also allowed. The following both statements are absolutely fine.
IN HTML5, you can also omit use of quotes around attribute values.
HTML Elements
An HTML file is made of elements. These elements are responsible for creating web pages and define content in that webpage. An element in HTML usually consist of a start tag <tag name>, close tag </tag name> and content inserted between them. Technically, an element is a collection of start tag, attributes, end tag, content between them.
Note: Some elements does not have end tag and content, these elements are termed as empty elements or self-closing element or void elements.
Such as:
Example
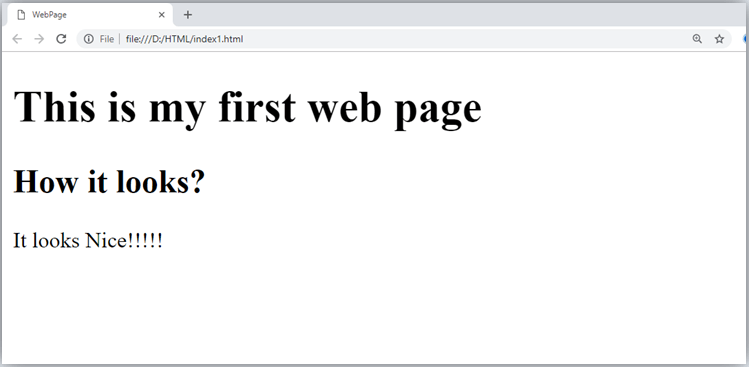
- All the content written between body elements are visible on web page.
Void element: All the elements in HTML do not require to have start tag and end tag, some elements does not have content and end tag such elements are known as Void elements or empty elements. These elements are also called as unpaired tag.
Some Void elements are <br> (represents a line break) , <hr>(represents a horizontal line), etc.
Nested HTML Elements: HTML can be nested, which means an element can contain another element.
Block-level and Inline HTML elements
For the default display and styling purpose in HTML, all the elements are divided into two categories:
- Block-level element
- Inline element
Block-level element:
- These are the elements, which structure main part of web page, by dividing a page into coherent blocks.
- A block-level element always start with new line and takes the full width of web page, from left to right.
- These elements can contain block-level as well as inline elements.
Following are the block-level elements in HTML.
<address>, <article>, <aside>, <blockquote>, <canvas>, <dd>, <div>, <dl>, <dt>, <fieldset>, <figcaption>, <figure>, <footer>, <form>, <h1>-<h6>, <header>, <hr>, <li>, <main>, <nav>, <noscript>, <ol>, <output>, <p>, <pre>, <section>, <table>, <tfoot>, <ul> and <video>.
Note: All these elements are described in later chapters.
Example:
Output:
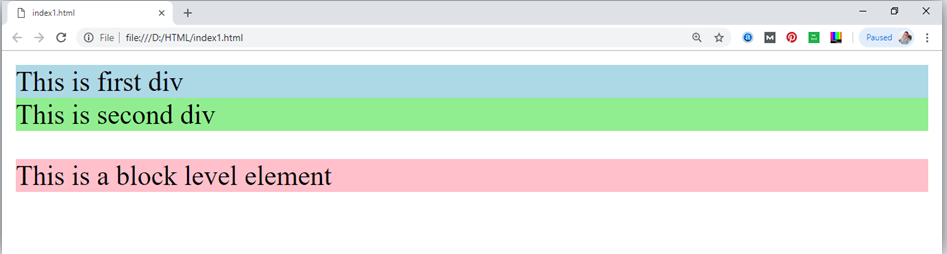
In the above example we have used
We have used style attribute which is used to styling the HTML content, and the background color are showing that it's a block level element.
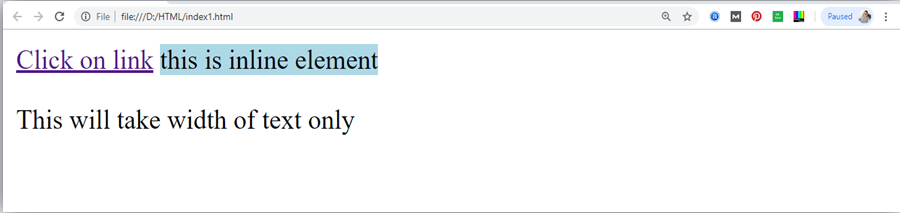
Inline elements:
- Inline elements are those elements, which differentiate the part of a given text and provide it a particular function.
- These elements does not start with new line and take width as per requirement.
- The Inline elements are mostly used with other elements.
<a>, <abbr>, <acronym>, <b>, <bdo>, <big>, <br>, <button>, <cite>, <code>, <dfn>, <em>, <i>, <img>, <input>, <kbd>, <label>, <map>, <object>, <q>, <samp>, <script>, <select>, <small>, <span>, <strong>, <sub>, <sup>, <textarea>, <time>, <tt>, <var>.
Example:
Output:
Following is the list of the some main elements used in HTML:
| Start tag | Content | End tag | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| <h1> ...... <h6> | These are headings of HTML | </h1>??..</h6> | These elements are used to provide the headings of page. |
| <p> | This is the paragraph | </p> | This element is used to display a content in form of paragraph. |
| <div> | This is div section | </div> | This element is used to provide a section in web page. |
| <br> | This element is used to provide a line break. ( void element) | ||
| <hr> | This element is used to provide a horizontal line. (void element) |
HTML Formatting
HTML Formatting is a process of formatting text for better look and feel. HTML provides us ability to format text without using CSS. There are many formatting tags in HTML. These tags are used to make text bold, italicized, or underlined. There are almost 14 options available that how text appears in HTML and XHTML.
In HTML the formatting tags are divided into two categories:
- Physical tag: These tags are used to provide the visual appearance to the text.
- Logical tag: These tags are used to add some logical or semantic value to the text.
NOTE: There are some physical and logical tags which may give same visual appearance, but they will be different in semantics.
Here, we are going to learn 14 HTML formatting tags. Following is the list of HTML formatting text.
| Element name | Description |
|---|---|
| <b> | This is a physical tag, which is used to bold the text written between it. |
| <strong> | This is a logical tag, which tells the browser that the text is important. |
| <i> | This is a physical tag which is used to make text italic. |
| <em> | This is a logical tag which is used to display content in italic. |
| <mark> | This tag is used to highlight text. |
| <u> | This tag is used to underline text written between it. |
| <tt> | This tag is used to appear a text in teletype. (not supported in HTML5) |
| <strike> | This tag is used to draw a strikethrough on a section of text. (Not supported in HTML5) |
| <sup> | It displays the content slightly above the normal line. |
| <sub> | It displays the content slightly below the normal line. |
| <del> | This tag is used to display the deleted content. |
| <ins> | This tag displays the content which is added |
| <big> | This tag is used to increase the font size by one conventional unit. |
| <small> | This tag is used to decrease the font size by one unit from base font size. |
1) Bold Text
HTML<b> and <strong> formatting elements
The HTML <b> element is a physical tag which display text in bold font, without any logical importance. If you write anything within <b>............</b> element, is shown in bold letters.
See this example:
Output:
Write Your First Paragraph in bold text.
The HTML <strong> tag is a logical tag, which displays the content in bold font and informs the browser about its logical importance. If you write anything between <strong>???????. </strong>, is shown important text.
See this example:
Output:
This is an important content, and this is normal content
Example
2) Italic Text
HTML <i> and <em> formatting elements
The HTML <i> element is physical element, which display the enclosed content in italic font, without any added importance. If you write anything within <i>............</i> element, is shown in italic letters.
See this example:
Output:
Write Your First Paragraph in italic text.
The HTML <em> tag is a logical element, which will display the enclosed content in italic font, with added semantics importance.
See this example:
Output:
This is an important content, which displayed in italic font.
3) HTML Marked formatting
If you want to mark or highlight a text, you should write the content within <mark>.........</mark>.
See this example:
Output:
I want to put a Mark on your face
4) Underlined Text
If you write anything within <u>.........</u> element, is shown in underlined text.
See this example:
Output:
Write Your First Paragraph in underlined text.
5) Strike Text
Anything written within <strike>.......................</strike> element is displayed with strikethrough. It is a thin line which cross the statement.
See this example:
Output:
Write Your First Paragraph with strikethrough.
6) Monospaced Font
If you want that each letter has the same width then you should write the content within <tt>.............</tt> element.
Note: We know that most of the fonts are known as variable-width fonts because different letters have different width. (for example: 'w' is wider than 'i'). Monospaced Font provides similar space among every letter.
See this example:
Output:
Hello Write Your First Paragraph in monospaced font.
7) Superscript Text
If you put the content within <sup>..............</sup> element, is shown in superscript; means it is displayed half a character's height above the other characters.
See this example:
Output:
Hello Write Your First Paragraph in superscript.
8) Subscript Text
If you put the content within <sub>..............</sub> element, is shown in subscript ; means it is displayed half a character's height below the other characters.
See this example:
Output:
Hello Write Your First Paragraph in subscript.
9) Deleted Text
Anything that puts within <del>..........</del> is displayed as deleted text.
See this example:
Output:
10) Inserted Text
Anything that puts within <ins>..........</ins> is displayed as inserted text.
See this example:
Output:
Delete your first paragraph.Write another paragraph.
11) Larger Text
If you want to put your font size larger than the rest of the text then put the content within <big>.........</big>. It increase one font size larger than the previous one.
See this example:
Output:
Hello Write the paragraph in larger font.
12) Smaller Text
If you want to put your font size smaller than the rest of the text then put the content within <small>.........</small>tag. It reduces one font size than the previous one.
See this example:
Output:
Hello Write the paragraph in smaller font.
HTML Heading
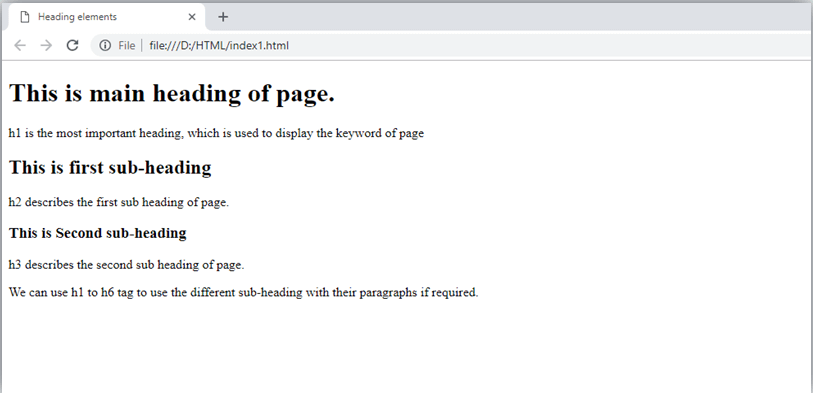
A HTML heading or HTML h tag can be defined as a title or a subtitle which you want to display on the webpage. When you place the text within the heading tags <h1>.........</h1>, it is displayed on the browser in the bold format and size of the text depends on the number of heading.
There are six different HTML headings which are defined with the <h1> to <h6> tags, from highest level h1 (main heading) to the least level h6 (least important heading).
h1 is the largest heading tag and h6 is the smallest one. So h1 is used for most important heading and h6 is used for least important.
Headings in HTML helps the search engine to understand and index the structure of web page.
Note: The main keyword of the whole content of a webpage should be display by h1 heading tag.
See this example:
Output:
Heading no. 1
Heading no. 2
Heading no. 3
Heading no. 4
Heading no. 5
Heading no. 6
Heading elements (h1....h6) should be used for headings only. They should not be used just to make text bold or big.
- HTML headings can also be used with nested elements. Following are different codes to display the way to use heading elements.
Example:
Output:
Supporting Browsers
| Element |  Chrome Chrome |  IE IE |  Firefox Firefox |  Opera Opera |  Safari Safari |
| <h1> to <h6> | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
HTML Paragraph
HTML paragraph or HTML p tag is used to define a paragraph in a webpage. Let's take a simple example to see how it work. It is a notable point that a browser itself add an empty line before and after a paragraph. An HTML <p> tag indicates starting of new paragraph.
Note: If we are using various <p> tags in one HTML file then browser automatically adds a single blank line between the two paragraphs.
See this example:
Output:
This is first paragraph.
This is second paragraph.
This is third paragraph.
Space inside HTML Paragraph
If you put a lot of spaces inside the HTML p tag, browser removes extra spaces and extra line while displaying the page. The browser counts number of spaces and lines as a single one.
Output:
I am going to provide you a tutorial on HTML and hope that it will be very beneficial for you.
Look, I put here a lot of spaces but I know, Browser will ignore it.
You cannot determine the display of HTML
because resized windows may create different result.
As you can see, all the extra lines and unnecessary spaces are removed by the browser.
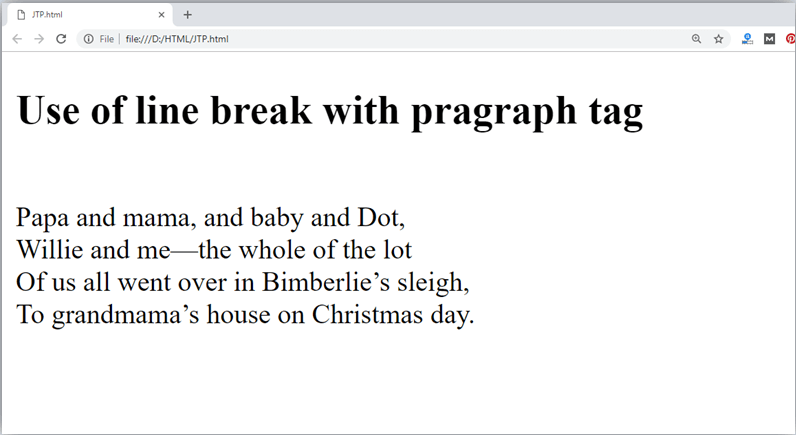
How to Use <br> and <hr> tag with paragraph?
An HTML <br> tag is used for line break and it can be used with paragraph elements. Following is the example to show how to use <br> with <p> element.
Example:
Output:
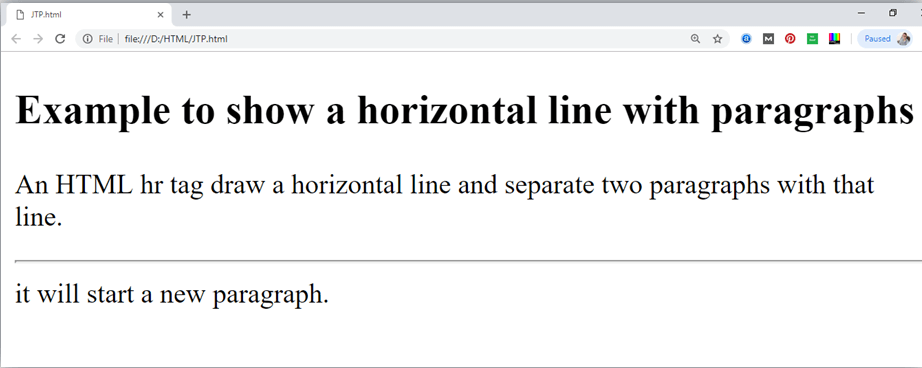
An HTML <hr> tag is used to apply a horizontal line between two statements or two paragraphs. Following is the example which is showing use of <hr> tag with paragraph.
Example:
Output:
Supporting Browsers
| Element |  Chrome Chrome |  IE IE |  Firefox Firefox |  Opera Opera |  Safari Safari |
| <p> | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
HTML Phrase tag
The HTML phrase tags are special purpose tags, which defines the structural meaning of a block of text or semantics of text. Following is the list of phrase tags, some of which we have already discussed in HTML formatting.
- Abbreviation tag : <abbr>
- Acronym tag: <acronym> (not supported in HTML5)
- Marked tag: <mark>
- Strong tag: <strong>
- Emphasized tag : <em>
- Definition tag: <dfn>
- Quoting tag: <blockquote>
- Short quote tag : <q>
- Code tag: <code>
- Keyboard tag: <kbd>
- Address tag: <address>
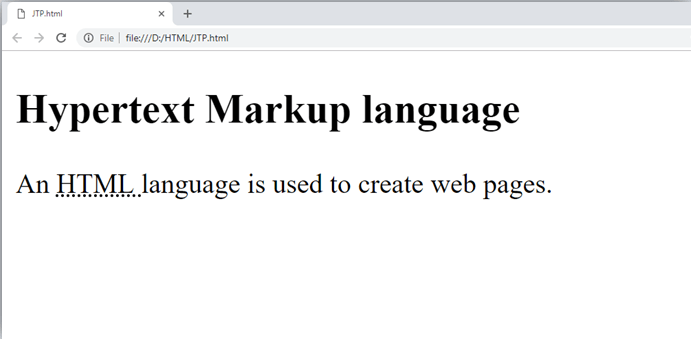
1. Text Abbreviation tag
This tag is used to abbreviate a text. To abbreviate a text, write text between <abbr> and </abbr> tag.
Example
Output:
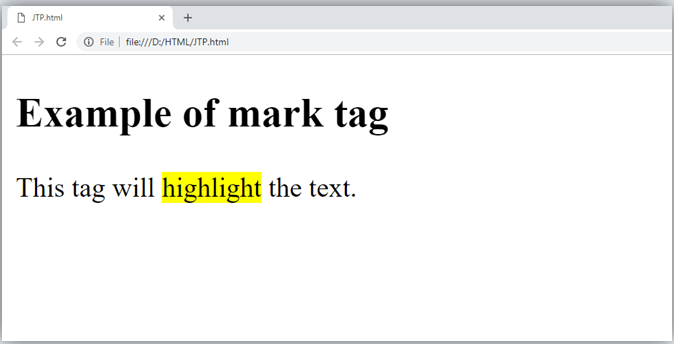
2. Marked tag:
The content written between <mark> and </mark> tag will show as yellow mark on browser. This tag is used to highlight a particular text.
Example
Output:
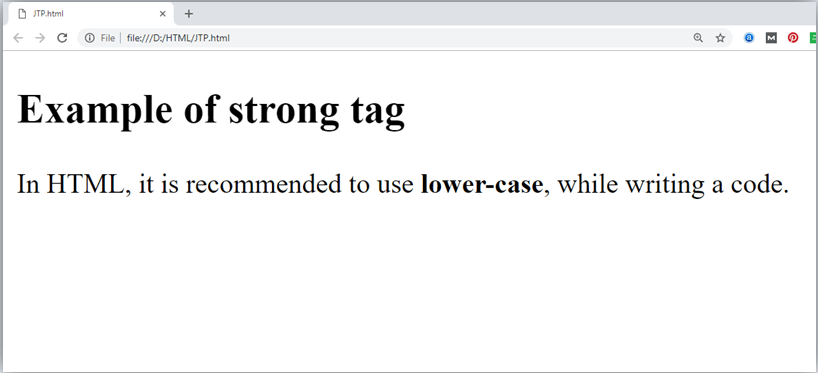
3. Strong text:
This tag is used to display the important text of the content. The text written between <strong> and </strong> will be displayed as important text.
Example
Output:
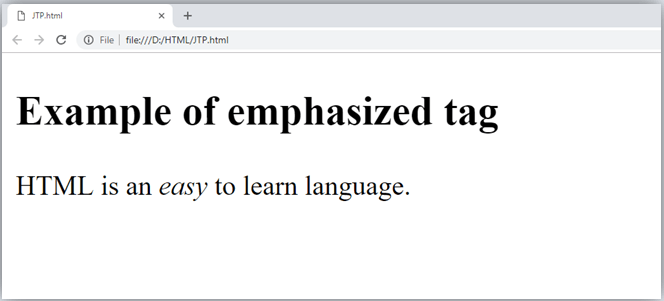
4. Emphasized text
This tag is used to emphasize the text, and displayed the text in italic form. The text written between <em> and </em> tag will italicized the text.
Example
Output:
5. Definition tag:
When you use the <dfn> and </dfn> tags, it allow to specify the keyword of the content. Following is the example to show how to definition element.
Example
Output:
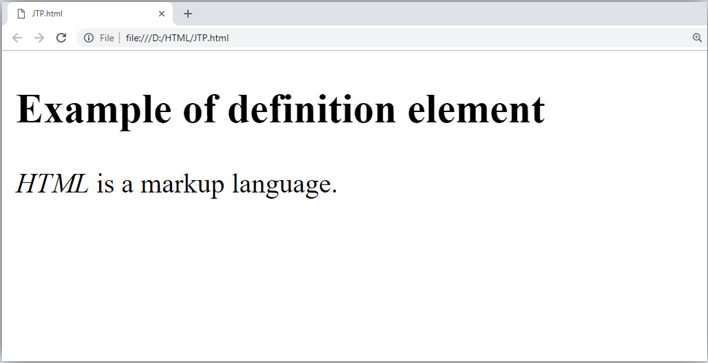
6. Quoting text:
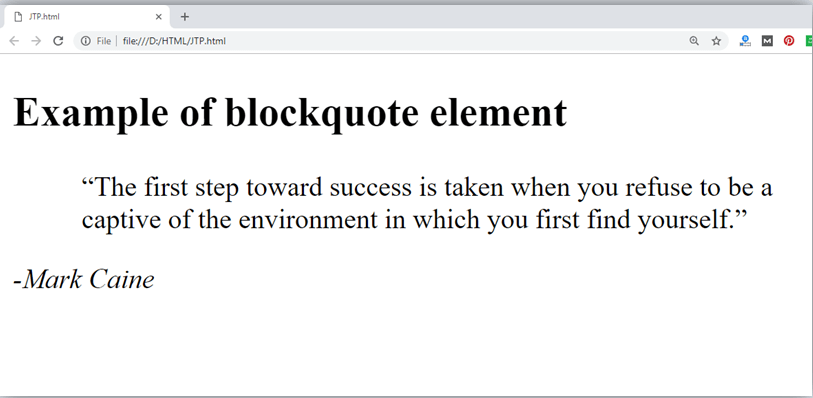
The HTML <blockquote> element shows that the enclosed content is quoted from another source. The Source URL can be given using the cite attribute, and text representation of source can display using <cite> ..... </cite>element.
Example
Output:
7. Short Quotations:
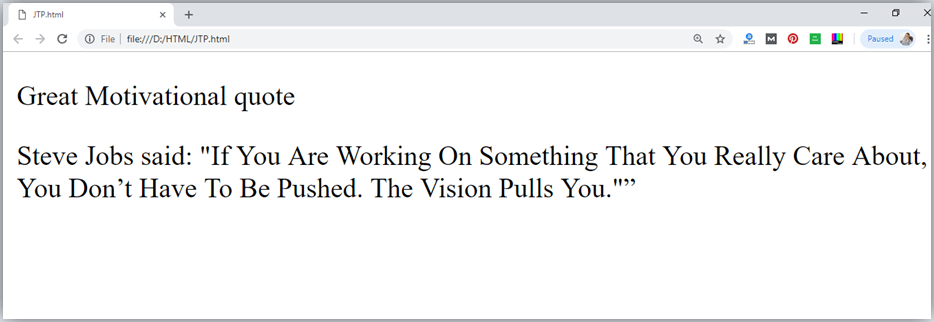
An HTML <q> ....... </q> element defines a short quotation. If you will put any content between <q> ....... </q>, then it will enclose the text in double quotes.
Example:
Output:
8. Code tags
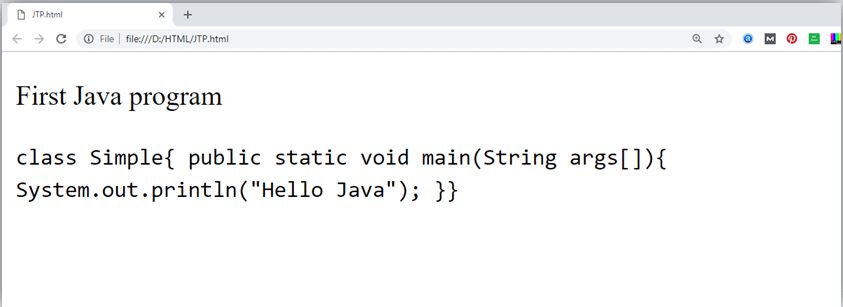
The HTML <code> </code> element is used to display the part of computer code. It will display the content in monospaced font.
Output:
9. Keyboard Tag
In HTML the keyboard tag, <kbd>, indicates that a section of content is a user input from keyboard.
Output:
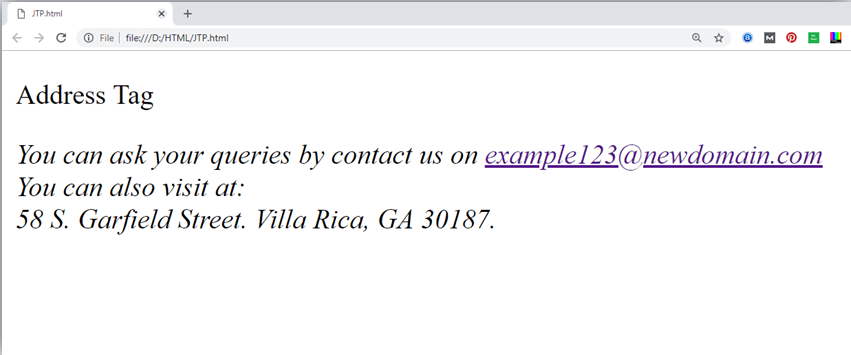
10. Address tag
An HTML <address> tag defines the contact information about the author of the content. The content written between <address> and </address> tag, then it will be displayed in italic font.
Output: